A 2009 Oxfam paper puts forth the view that scaling-up private healthcare provision is very unlikely to deliver high-quality care to the poor. Commenting on the paper, Jishnu Das contends that while it is right to argue for investments that improve public healthcare and build State capacity, we will not get there by demonising the private sector.
As a researcher working on health and education over the last 15 years, I read your 2009 paper on the dangers of private healthcare in low- and middle-income countries with great interest. I admire the strength of your convictions, but worry that your inaccurate reading of the literature (‘what do we know about private health care?’) detracts from your normative question (‘what kinds of health systems should we aspire to in a world that is fair?’), leaving readers confused about what to believe.
To be clear, I agree that if we want a world where the poor can access high-quality care, private markets do not offer an easy ‘out’ from much needed investments in the public sector. However, this is not because the private sector provides worse care than the public sector, as you suggest on pages 19 to 21 of your report. All the available evidence (the little there is) suggests that primary care is either equivalent or higher quality in the private sector.
I support these claims in reverse.
What do we know about private sector primary care?
Publications on healthcare are often compared to a gushing hydrant from which we try to sip while keeping dry. Sometimes, though, you have to get wet to know what you are drinking.
Take quality of care in the public and private sectors.
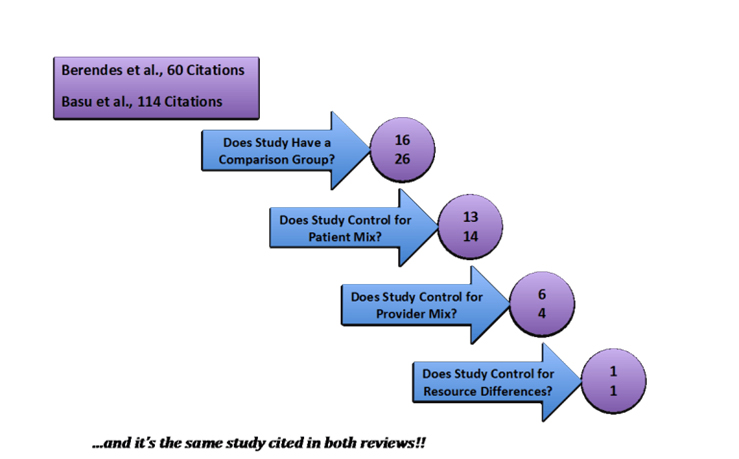
Two systematic reviews on the topic (Berendes et al. 2011 and Basu et al. 2012), published only one year apart in PLoS Medicine, arrived at precisely opposite conclusions. To untangle this puzzle, my co-authors, Jorge Coarasa, Liz Gummerson, Asaf Bitton, and I read all the papers covered in these reviews and found that:
- Although the methodologies and the literature covered differed, both reviewers chose decisions that were defensible and sensible: The reviews scored equally on the AMSTAR[1] checklist, which evaluates the quality of systematic reviews.
- However, the quality of the studies included in these reviews varied enormously. Ultimately, there were only 44 studies with data on both the public and the private sector and, as we argue, only one study (included in both reviews) that came close to using the right comparison.
In Coarasa et al. 2017, we suggest four criteria for a high quality comparative study (see Figure 1). Only a single study from Thailand passed all of these requirements. However, even that study may be considered flawed as (A) similar, but not identical providers were studied, leading to potential selection bias[2] on unobserved characteristics and (B) the case (depicted by standardised patients or “mystery clients”) was too hard − no one got it right, leaving the researchers to base their conclusions entirely on the comparative use of unnecessary medicines.
- The sample should include both public and private providers (sounds sensible if we want to say something about their relative performance).
- The sample should compare similar providers. In India, most private providers have no medical training and most public providers have four or more years of training. A simple comparison of the average public and average private provider conflates the effect of training with the effect of the sector. Studies based on household surveys like the DHS (Demographic and Health Surveys) fail on this regard, since we do not know the characteristics of the health provider visited.
- The study should do something to control for case and patient-mix. You don’t want to compare a public sector provider who sees very sick patients with a private sector provider who doesn’t.
- The study should try to account for differential constraints. Caseload and infrastructure are examples: Perhaps the public sector provider sees many more patients than the private sector provider or has access to worse infrastructure.
Figure 1. Imposing sensible requirements on studies of public-private comparisons reduces the number of studies to…..ONE
In my work with Alaka Holla, Aakash Mohpal, and Karthik Muralidharan, we sent standardised patients to public and private providers in representative samples in the state of Madhya Pradesh in India. This satisfied criteria (1) and (3), but not (2). In fact, in our sample private providers are mostly untrained while public providers are (theoretically) fully trained. To address (2) we took the sample of public providers who had dual practices (more than 80%) and sent standardised patients to both their public and private clinics. Finally, on (4) providers had better access to equipment (for all types of equipment) in their public compared to private clinics. But in both their public and private clinics, there was enormous excess capacity, so that very high caseload was almost never a constraining factor on their practice.
Here is what we found:
- Standardised patients received similar care in public clinics and from private providers, the majority of whom were untrained. This was not because training had no value, but because in 64% of cases the patients in public clinics also saw an untrained person, often because doctors were on leave or absent.
- Standardised patients received more correct treatment from fully trained providers in the public sector than from the average provider in the private sector. But they also received more unnecessary antibiotics.
- Standardised patients receive more correct treatment from the same provider in their private than from their public clinics. There was no difference in the use of unnecessary antibiotics across the two.
It would be a mistake to dismiss these findings as only pertinent to a single state in a single country. New information has enormous value when the results are unexpected. The onus is now on others to replicate this methodology in other locations. (We have already replicated parts of this design in West Bengal in Das et al. 2016a, and in Nairobi, Kenya in Daniels et al. 2017.)
Others may argue that the private sector is different from private providers. That is, why not compare the average private provider to the fully trained public provider? The problem with doing so is that you end up comparing rural private providers to urban or peri-urban public providers. If there are no public providers in the village where the private provider is located, the relevant counterfactual may be ‘no care’ or ‘self-care’ rather than public-sector care. This is a systematic issue with your report − less than fully qualified providers may not provide great quality. But the right question is: Compared to what alternative?
You based the positive parts of your paper on thin evidence. You have risked leaving your audience wondering whether your advocacy rather than the (lack of) evidence guides your views.
Should we rely on the private sector to scale-up care to the poor?
Private systems provide what patients want and what patients can pay for. Outside of healthcare, we accept the ability of private systems to allocate scarce resources according to people’s wants, but are unhappy with the vast inequality at the starting block. With healthcare, we have also been unhappy with allocations based on what people want and have therefore sought to transfer more power from patients to doctors and administrators. Recent work has started to challenge the idea that patients do not know what is good for them, or that transferring power to doctors makes things better, but legitimate concerns remain.
Like you, I disagree.
My disagreement is with the notion that you can address the problem of limited State capacity by substituting provision with regulation. Regulation may be equally hard − or even harder − than provision. This was one of the big lessons I learned working with India’s health insurance programme, RSBY (Rashtriya Swasthya Bima Yojna). The big problem that we faced − and never really solved − was how to correctly price different services that were covered under insurance.
These prices are critical. The main mechanism the private sector uses to provide incentives and allocate scarce resources is the price of care. In healthcare, quality is scarce and, as we show, providers who correctly treat patients charge higher fees. Otherwise, no provider would have an incentive to provide higher quality. But poor people cannot afford higher quality, and therefore are priced out of the market.
The idea that we can fix this with a set of price subsidies is likely a mirage.
First, an organisation with regular administrative and data systems will have to set the prices. Such an organisation has to figure out thorny questions like whether there should be a uniform price for all providers in the region (thus breaking the chain of accountability to patients that keeps the private sector in check) or whether they should continue to subsidise providers at market prices (in which case they have to worry about how the price subsidy will affect the equilibrium market price). To believe that a State with low capacity will be able to address these hard problems is wishful thinking. In the US, administrative costs are much higher and an industry of medical coders (here are some of the degrees you can get) figures out precisely how to manipulate the price schedule to make more money for their clinic.
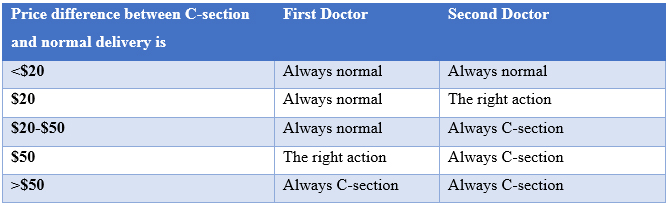
Even if countries were able to solve the problem of designing price systems, the peculiarities of healthcare may make it impossible to ever get the prices right. How should they price to ensuring that patients get what they need and do not get what they don’t need? One option is to keep markups (or profits) identical irrespective of the action. For instance, if the cost of a C-section is US$150 and the cost of a normal delivery is US$100, and we priced these at US$200 and US$150, it would induce the doctor to ‘do the right thing’ because profits are the same regardless of actions.
Figure 2. When costs differ, a uniform price will not get you efficient outcomes
But now suppose there are two doctors. For the first, the costs are as before (US$150 for a C-section and US$100 for normal delivery), but for the second, the cost of the C-section is US$200 and the cost of normal delivery is US$180. As the table above shows, even if costs are observable, there is no uniform price at which both doctors do the right thing. Since decision-makers do not observe costs, this is a truly difficult problem.
Summary: No predictable winners
I agree that it is right to argue for investments that improve public care and build State capacity. At the same time, we will not get there by downplaying the enormous challenges we face or by demonising the private sector. There are some success stories (Sri Lanka, Thailand’s 30 Baht programmes (Gruber et al. 2014)) but there are also notable failures − in India, we can’t get public doctors to even come to work. Two very high profile attempts (Banerjee et al. 2008 and Dhaliwal and Hanna 2014) collapsed because nurses broke the attendance machines or doctors were not bothered. Moving beyond specific programmes or populations to more general care will be difficult in many countries. Ultimately, it may be that the inefficiencies from incorrect regulation in a price subsidy system are lower than what we can achieve with public sector reform. But the point is that there are no predictable winners here.
The correct message is that the private sector provides comparable or higher quality care than the public sector, but even with public subsidies, it will be extremely hard to use this advantage to provide care for the poor.
This article first appeared on the Brookings Blog: https://www.brookings.edu/blog/future-development/2017/06/07/a-letter-to-oxfam-reframing-the-questions-around-private-sector-health-care/.
Further Reading
- Berendes, Sima, Peter Heywood, Sandy Oliver and Paul Garner (2011), “Quality of Private and Public Ambulatory Health Care in Low and Middle Income Countries: Systematic Review of Comparative Studies”, PLoS Medicine, 8(4): e1000433.
- Banerjee, Abhijit V, Rachel Glennerster and Esther Duflo (2008), “Putting a band-aid on a corpse: Incentives for nurses in the Indian public health care system”, Journal of the European Economic Association, 6(2-3):487-500. Available here.
- Basu, Sanjay, Jason Andrews, Sandeep Kishore, Rajesh Panjabi and David Stuckler (2012), “Comparative Performance of Private and Public Healthcare Systems in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: A Systematic Review”, PLoS Medicine, 9(6): e1001244. Coarasa, Jorge, Jishnu Das, Elizabeth Gummerson and Asaf Bitton (2017), “A systematic tale of two differing reviews: evaluating the evidence on public and private sector quality of primary care in low and middle income countries”, Globalization and Health, 13(1):24
- Daniels, Benjamin,Amy Dolinger, Guadalupe Bedoya, Khama Rogo, Ana Goicoechea, Jorge Coarasa, Francis Wafula, Njeri Mwaura, Redemptar Kimeu and Jishnu Das (2017), “Use of standardised patients to assess quality of healthcare in Nairobi, Kenya: a pilot, cross-sectional study with international comparisons”, BMJ Global Health, 2, No. 2.
- Das, Jishnu, Abhijit Chowdhury, Reshmaan Hussam and Abhijit V Banerjee (2016a), “The impact of training informal health care providers in India: A randomized controlled trial”, Science, Vol. 354, Issue 6308.
- Das, Jishnu, Alaka Holla, Aakash Mohpal and Karthik Muralidharan (2016b), “Quality and Accountability in Health Care Delivery: Audit-Study Evidence from Primary Care in India”, American Economic Review, 106(12):3765-99.
- Dhaliwal, I and R Hanna (2014), ‘Deal with the Devil: The Successes and Limitations of Bureaucratic Reform in India’, NBER (National Bureau of Economic Research) Working Paper No. 20482.
- Gruber, Jonathan, Nathaniel Hendren and Robert M Townsend (2014), “The Great Equalizer: Health Care Access and Infant Mortality in Thailand”, American Economic Journal: Applied Economics, 6(1):91-107. Available here.
- Oxfam International (2009), ‘Blind Optimism: Challenging the myths about private health care in poor countries’, Oxfam briefing paper.
- Rosenthal, E (2017), ‘Those Indecipherable Medical Bills? They’re One Reason Health Care Costs So Much’, The New York Times Magazine, 29 March 2017.
Notes
- AMSTAR stands for A Measurement Tool to Assess Systematic Reviews. There has been a proliferation of systematic reviews as one of the key tools for evidence-based healthcare. It creates an environment where researchers can base decisions on accurate, succinct, credible, comprehensive and comprehensible summaries of the best available evidence on a topic thereby minimising error and bias. AMSTAR aims to be a valid, reliable and useable instrument that helps users in assessing the methodological quality of systematic reviews.
- Selection bias is the bias introduced by the selection of individuals, groups or data for analysis in such a way that proper randomisation is not achieved, thereby ensuring that the sample obtained is not representative of the population intended to be analysed.




 29 September, 2017
29 September, 2017 



Comments will be held for moderation. Your contact information will not be made public.